Getting to the Heart of Web3.0: A Practical Guide to This New Raging Evolution.
Web3.0 eliminates the significant pitfalls of the present web and its characteristics. It makes the following promises: security and transparency.
A stateless model is how the modern internet works. The power is concentrated in the hands of a few powerful people.
We do not have control over our data, which raises worries about privacy, security, and openness, among other things.
The internet that we have today, known as Web2, is based on the concept that the majority of data is stored and handled centrally on the servers of trusted institutions.
Every single contact leads to a copy of our data being sent to the server of an Internet service provider.
In the long run, Web 3.0 will enable the development of more intelligent, linked, open, and transparent websites in which power is spread and in the hands of everyone who participates in the process.
Web3 alters the backend architecture of the Internet by utilizing a number of blockchain networks, also known as distributed ledgers, to accomplish this.
Web3.0 eliminates all of the nonsense from the present web and its characteristics.
Web3.0 is, in many ways, a revolution in the backend.
It promises security, transparency, and privacy, as well as an intrinsic payment settlement layer through the use of cryptocurrencies, among other things.
Nonetheless, it should be noted that blockchain is not the only technology required to decentralize the internet.
Web3 has a broader scope, and blockchain is built on top of it to provide scalability.
Before we get into how blockchain will disrupt numerous industries, let's take a quick stroll through what blockchain is and how it works. Let's go ahead and do it.
A Layman's Guide to Blockchain Technology
Specifically, blockchain is a type of database that differs from a traditional database in the manner in which it saves information.
It contains information in the form of blocks that are linked together.
As a result of blockchain technology, decentralization is achieved in the sense that no single party has the power, but instead, all users together have the power.
What will be the changes in the Web's structural design?
Modern software (Web2) uses HTML, CSS, or JavaScript to render the frontend. The front-end of a webpage or a mobile application interacts with one or more centralized servers and databases on the backend
When you input your Facebook username and password, an API call is made to a centralized data to retrieve your personal data. These data on the server can be compromised by you or anyone with access, with ease.
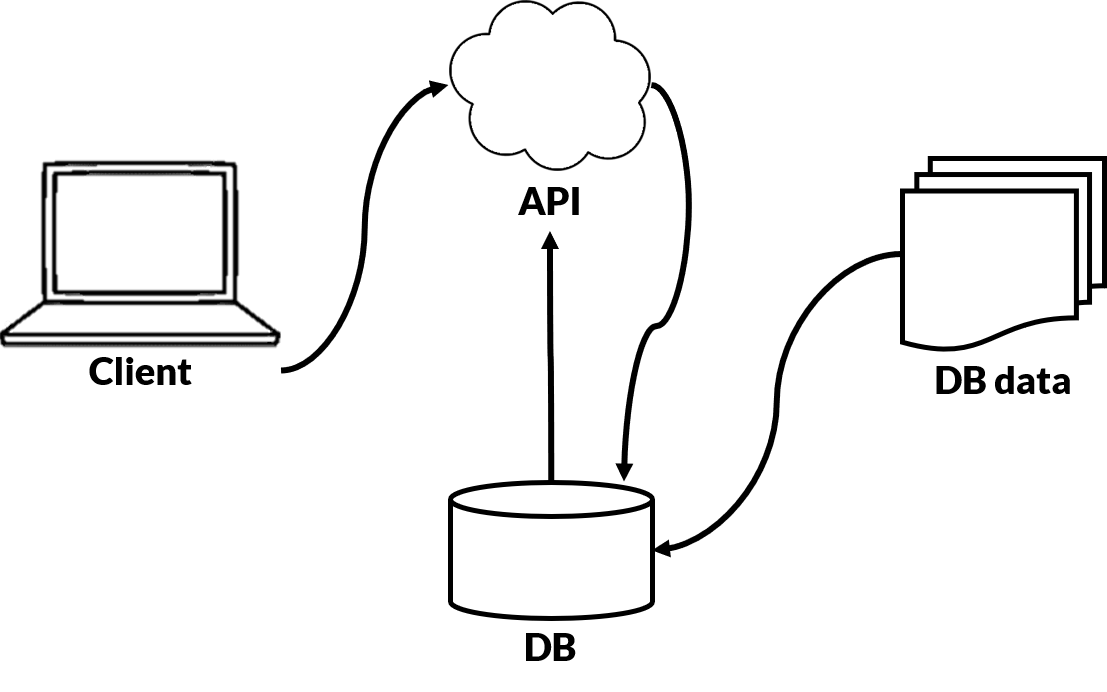
Instead of using a server and database, decentralized systems use the same frontend as Web2, but communication with a backend occurs through a blockchain network, i.e., smart contracts and peer-to-peer networks (which do not operate or run on the blockchain) instead of a server and database.
A client is the backend of the blockchain network that isn't controlled by anyone. It's called the "wallet" in some places.
The wallet is in charge of managing the public-private key pair and an address, which are used to provide network nodes with a unique and distinct identity and to let them to interact with the network.
Blockchain and the Software Development Industry
Blockchain technology is addressing various challenges faced in the software industry.
It ensures productive testing activities enhance collaboration within teams and increase the use of smart contracts in software development.
Ethereum has gained a unique niche for itself in the crypto space as a smart contract platform.
The skyrocketing demand for blockchain-related jobs also translated into a significant salary bump.
The average salary for blockchain devs is $150,000 - $175,000 approximately $15,000 - $40,000 higher than the standard salary for software engineers.
High salaries for workers in blockchain are a function of increased demand and short supply due to the fact that the technology is pretty shiny and new and there aren't a lot of people ready to fill up the jobs.
The transition from centralized Web2 to the decentralized web will be a gradual process because it is no doubt that decentralized architectures are more resilient than the currently predominant centralized Web2 but they are also slower.
Speed, performance, and usability are drawbacks in the Web3 that will very likely be resolved over time, once the core components of the Web3 are scaled and more work is invested.
Decentralization promises something spectacular from what we are used to even though not every single thing needs to be decentralized.
It is no doubt that a large proportion of the internet will be decentralized, however centralized architectures have advantages and will most probably be around, at least for specific use cases.
The Impeccable Security Blockchain can help.
There are numerous ways in which blockchain technology addresses the concerns of security and trust. New blocks are stored in a linear and chronological fashion, and new blocks are stored in a chronological and linear fashion (always added to the end of the blockchain).
A block that has been added to the end of the blockchain is very difficult to go back and change the contents unless all of the users come to a unanimous agreement on the need to do so.
This is why cybersecurity is considered one of the most potential areas for the development of blockchain technology.
Businesses of all sizes will confront ever-increasing problems as a result of the threat of data hacking, which will only become worse. Blockchain technology has the potential to protect against such attacks.
Conclusion
It should be highlighted, however, that Web3.0 is a very fluid idea that is expected to evolve at an alarming rate over the next years.
Today, the majority of notions are predefined, and many things are on the verge of change.
As such, anyone interested in entering the blockchain must be hardwired to constantly reinvent themselves in order to remain relevant.
The following is a list of excellent books that will assist you in getting started with blockchain and smart contract creation.
The Infinite Machine How an Army of Crypto-hackers Is Building the Next Internet with Ethereum by Camila Russo
The Spatial Web How Web 3.0 Will Connect Humans, Machines and AI to Transform the World by Gabriel René Dan Mapes
Mastering Ethereum Building Smart Contracts and DApps by Andreas M. Antonopoulos, Gavin Wood Ph. D.
How to Defi by CoinGecko Lau, Darren Lau, Daryl The, Sze Jin Kho, Kristian Azmi, Erina Lee, TM Ong, Bobby
Learn More
This blog is dedicated to educating curious individuals who want to learn about technology and improve their skills.
Check out the blog to show your support.

